- A High School GPA Calculator turns grades + credits into weighted and unweighted GPA in seconds.
- Credits change the math. A 1.0-credit class matters more than a 0.5-credit class.
- Weighted GPA can go above 4.0 if your school adds points for Honors, AP, IB, or Dual Enrollment.
- GPA mismatches are common because schools use different scales, rounding, and weighting rules.
- Colleges often recalculate GPA, so strong grades in hard classes still matter a lot.
What a high school GPA really measures
Your GPA is a number that summarizes your grades across classes. Schools use it to compare students and track progress. Colleges also look at it, but many schools do their own math using your transcript grades.
GPA works best when you treat it like a scoreboard, not your identity. A strong GPA shows you can handle school work over time. It also helps with class rank, honors, and scholarships in many districts.
The tricky part is that “GPA” is not one universal number. A 3.8 at one school can mean something different at another. That is why it helps to know your scale, your credits, and whether your school uses weighted or unweighted GPA.
To learn the exact math behind it, use the GPA formula guide in the GPA formula explained guide and the plain-language breakdown in how to calculate GPA.
Use a High School GPA Calculator to avoid math mistakes
Manual GPA math looks easy until small details stack up. One missed 0.5 credit, one wrong grade-point value, or one extra Honors bonus can change your final number. A High School GPA Calculator helps you stay consistent.
A good calculator lets you enter:
- Course name
- Grade (letter or percent)
- Credits (1.0, 0.5, or other)
- Course level (Regular, Honors, AP/IB, Dual Enrollment)
Then it outputs term GPA and cumulative GPA, plus weighted and unweighted versions.
This saves time during busy weeks, like midterms and finals. It also helps you run “what-if” checks before you pick classes for next year.
You can use the main tool on the homepage: High School GPA Calculator. For a focused walkthrough, see high school GPA calculator guide and the full method in how to calculate high school GPA.
Choose the right grading scale for your school
Your GPA depends on the grading scale your school uses. Many students guess the scale and get the wrong answer. Schools can use:
- Straight letter grades (A=4.0, B=3.0)
- Plus/minus grades (A-=3.7, B+=3.3)
- Percent-to-point scales (like 92%=3.7 in some systems)
- Different cutoffs (some schools need 93% for an A)
Even one cutoff change can shift your GPA across every class. That is why the first step is always the same: match your calculator to your school’s rules.
If your transcript lists grade points, trust those numbers. If it only lists letters or percents, check your student handbook or ask counseling.
For examples across common systems, use the chart in high school grading scales chart. If you need quick conversions, use letter to point GPA conversion and percentage to 4.0 GPA conversion.
Turn letter grades into grade points fast
A GPA is built from grade points, not letter grades. Your job is to convert each course grade into the correct point value for your school.
Here is a simple example on a 4.0 scale:
| Letter grade | Grade points |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| B | 3.0 |
| C | 2.0 |
| D | 1.0 |
| F | 0.0 |
Plus/minus systems add more detail, like 3.7 for A- or 3.3 for B+. That can help schools separate close grades. It also makes calculator errors more likely if you pick the wrong system.
If your transcript uses percent grades, convert percent → letter → points. Some districts do a direct percent → points method, so ask before you assume.
For accurate conversions, keep these tools bookmarked: letter to point GPA conversion guide and GPA conversion charts and tools. If you want deeper context, see types of GPA scales.
Credits matter more than most students think
Credits decide how much each class “counts” in the final average. Many high schools use:
- 1.0 credit for full-year classes
- 0.5 credit for semester classes
- 0.25 credit for quarter classes (some schools)
If you treat every class the same, you can end up with a GPA that looks close but still wrong.
Here is the key idea: a 1.0-credit class has double the weight of a 0.5-credit class. That matters a lot if your schedule mixes semester electives with yearlong core classes.
Credits also affect weighted GPA. An AP class with extra points can lift your GPA more if it carries more credits.
If you are unsure about credits, check your transcript line-by-line. Then use the guide in credit hour weighting GPA guide and the full walkthrough in credits and course level input guide.
Quality points: the number behind every GPA
Most schools calculate GPA using quality points. Quality points combine grade points and credits into one value.
The rule is simple:
- Quality points = grade points × credits
Then you add them up and divide by total credits.
Example idea:
- You earn an A (4.0) in a 1.0-credit class → 4.0 quality points
- You earn an A (4.0) in a 0.5-credit class → 2.0 quality points
Same letter grade. Different impact.
This is why GPA calculators ask for credits. Without credits, the calculator can only guess, and guessing leads to mismatches.
If you want the cleanest explanation with examples, read quality points vs GPA explained. For the full formula, see GPA formula guide. If you want a tool that matches the math, use the high school GPA calculator.
Unweighted GPA: simple and capped at 4.0
Unweighted GPA gives every class the same level. It does not care if you took AP Chemistry or regular Chemistry. An A is an A.
Unweighted GPA is great for a quick snapshot because it feels fair and easy to compare. It also stays on a 0.0 to 4.0 scale in most schools.
Students like unweighted GPA because it answers one clear question: How strong are my grades overall? If your unweighted GPA is high, it means your grades stay steady across subjects.
The downside is that it does not reward challenge. Two students can have the same unweighted GPA even if one took harder classes.
To compare both systems side-by-side, read weighted vs unweighted GPA guide and the quick explainer in weighted vs unweighted GPA. If you want to run both numbers in one place, use weighted vs unweighted GPA calculator.
Weighted GPA: honors and AP can push it above 4.0
Weighted GPA adds extra points for harder classes. Schools do this to reward course rigor, not just high grades.
Many schools add something like:
- Honors: +0.5 points
- AP/IB: +1.0 points
So an A in AP might count as 5.0 instead of 4.0 on some scales. That is why weighted GPA can go above 4.0.
Weighted GPA helps colleges see that you challenged yourself. It also matters for class rank in many schools.
Still, weighting rules are not universal. Some schools cap weighted GPA, and some only weight certain subjects. That is why you should always match your calculator to your district rules.
For clear rules and examples, use GPA weighting guide for Honors and AP and weighted GPA myths debunked. To compare outcomes across scales, try 4.0 vs 5.0 GPA outcome simulator.
How schools weight Honors, AP, IB, and Dual Enrollment
Course level matters because it changes grade points in weighted systems. Most schools group classes into levels like:
| Course level | Typical bonus | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regular | +0.0 | English 10 |
| Honors | +0.5 | Honors Algebra II |
| AP / IB | +1.0 | AP Biology |
| Dual Enrollment | varies | College Composition |
Dual Enrollment weighting is the most confusing. One district may weight it like AP. Another may treat it like regular. Some schools only weight it if it matches a core subject.
IB can also vary. Some schools weight HL classes more than SL classes. Some do not.
If you take IB classes or move between districts, use a converter that fits your system. Helpful tools include IB to GPA conversion guide and how school districts calculate GPA.
If you want one page that explains how to input course types correctly, use credits and course level input guide and GPA weighting guide honors AP.
Common grading scale differences that change your GPA
Two students can earn the same percent grades and still get different GPAs. That happens because grading scales can change in small ways that matter.
Common differences include:
- Different A cutoffs (90% vs 93%)
- Plus/minus systems (A- vs A)
- Different rounding (3.495 becomes 3.49 or 3.50)
- Different class types included (electives may count or not)
These details can shift GPA by 0.1 to 0.3 without any “real” grade change. That can feel unfair, but it is normal in the US school system.
If you want a clean reference, keep the chart from high school grading scales chart nearby. For percent-based conversions, use 100 point to 5 point conversion and GPA scale comparison.
A mismatch does not mean you failed. It often means your calculator used a different rule than your school used.
Why your GPA does not match your transcript
A transcript mismatch is one of the most common GPA problems. You calculate a number, and your school shows a different one. That usually happens for a few clear reasons.
Common causes:
- Your school uses weighted GPA, but you calculated unweighted
- You forgot a 0.5-credit class or counted it wrong
- Your school uses plus/minus points, and you used a simple 4.0 scale
- Your school rounds differently
- Your school excludes pass/fail or certain electives
- Your school uses semester vs yearly averaging in a special way
The fastest fix is to copy your transcript into a calculator that supports credits and course level.
If you want a full list of causes, use why GPA does not match transcript and common GPA calculation errors to avoid. For pass/fail rules, check how pass/fail grades impact your GPA.
Fix a GPA mismatch with a quick transcript audit
You can debug a mismatch like you debug a math problem. You do not need to panic. You only need to check the inputs.
Start with a quick audit:
- Verify every course grade matches the transcript
- Verify every credit value (1.0 vs 0.5)
- Mark each course level: Regular, Honors, AP/IB, Dual Enrollment
- Remove pass/fail courses if your district excludes them
- Check if your school uses semester GPA, year GPA, or both
Then re-run the calculation.
If your number still does not match, your school may apply a special rule. Some districts weight only core classes. Some cap weighted GPA. Some use class rank GPA that differs from transcript GPA.
For a structured checklist, use transcript GPA audit guide and how school districts calculate GPA. If you want a tool that matches those rules, use high school GPA calculator.
Track term GPA vs cumulative GPA the right way
Students often mix up term GPA and cumulative GPA. Both matter, but they answer different questions.
- Term GPA = your GPA for one grading period (semester or trimester)
- Cumulative GPA = your GPA across all completed terms
Term GPA helps you spot changes fast. If your grades drop this semester, term GPA shows it right away. Cumulative GPA moves slower because it averages your whole history.
If your school uses trimesters, the math can look different from semesters. A strong way to stay accurate is to calculate each term, then roll it into one total.
Tools that help:
- semester GPA calculator for standard schedules
- trimester GPA calculator for trimester schools
- cumulative GPA calculator to combine everything
If you want to visualize progress, use GPA trend graph generator.
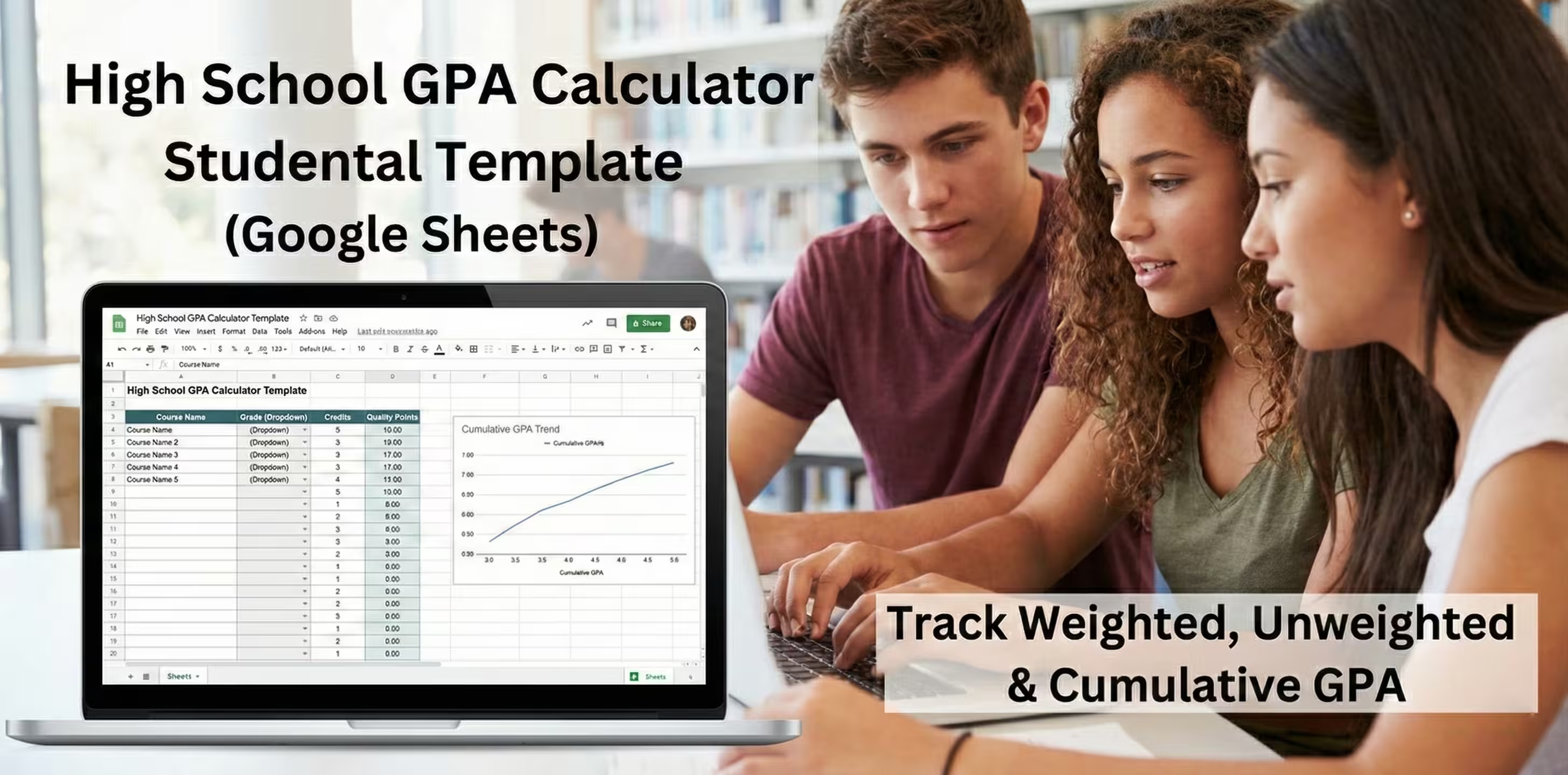
Build a Google Sheets tracker for GPA planning
A spreadsheet tracker gives you control. It also helps you plan goals before grades lock in. You can build one in Google Sheets in under an hour and keep it updated all year.
A good sheet includes:
- Course name
- Grade
- Course level
- Credits
- Grade points
- Quality points
- Term total and cumulative total
You can also add a “goal” column, like “raise to B+” or “keep A.” That turns your GPA into a plan, not a mystery.
If you want a ready template, start here: high school GPA calculator template Google Sheets. For the math behind it, use quality points vs GPA explained and credit hour weighting GPA guide.
How colleges read GPA and why they recalculate
Colleges want fairness across thousands of high schools. That is hard because schools use different scales, cutoffs, and weighting rules. So many colleges recalculate GPA from your transcript.
That means they often:
- Focus on core subjects (math, science, English, history, language)
- Ignore some electives
- Use one consistent scale for all students
- Look at course rigor, not only the GPA number
This is great news if your school has a tough scale. A slightly lower GPA at a harder school can still look strong when colleges standardize it.
Your job is to show a clear academic story:
- Solid grades
- Hard courses when you can handle them
- Improvement over time
If you plan to apply to competitive programs later, review real benchmarks in GPA requirements for college admissions and the broader view in GPA benchmarks for professional programs.
Use GPA goals and study habits that raise grades
A GPA calculator shows the number. Your habits change the number. If you want a higher GPA, focus on actions that raise grades in real life.
High-impact habits that work:
- You write every due date in one place
- You review notes the same day you take them
- You start big projects early, even with 15 minutes
- You ask teachers for help before you fall behind
- You fix weak spots from quizzes, not just homework
Small changes can lift one class from a C+ to a B-. That can move your GPA more than you think, especially in 1.0-credit core classes.
If you want a practical checklist, use study tips for better grades and study habit audit checklist. If you want a clear plan to raise your number, use raise my GPA action plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a High School GPA Calculator?
A High School GPA Calculator is a tool that turns your grades + credits + course level into a GPA. A strong calculator gives you weighted GPA and unweighted GPA, plus term and cumulative views. You can try the main tool here: High School GPA Calculator and learn the inputs in high school GPA calculator guide.
Can a high school GPA be higher than 4.0?
Yes. A GPA above 4.0 usually means your school uses weighted GPA and adds points for advanced classes. Learn the difference in weighted vs unweighted GPA guide and see how bonuses work in GPA weighting guide honors AP.
Why is my calculated GPA different from my transcript GPA?
Mismatches happen when your calculator uses different rules than your school. Credits, plus/minus grades, weighting, rounding, and excluded classes can all change the result. Use why GPA does not match transcript and double-check with common GPA calculation errors to avoid.
Do pass/fail classes count in high school GPA?
Many schools exclude pass/fail from GPA math, but rules vary by district. If you include a pass/fail class by mistake, your GPA can shift. Check your policy using how pass/fail grades impact your GPA and confirm your district method in how school districts calculate GPA.
How do I calculate semester GPA vs cumulative GPA?
Semester GPA uses only one term. Cumulative GPA combines all terms and credits. If you want the right tool for each job, use semester GPA calculator and cumulative GPA calculator. If you want to track changes over time, try GPA trend graph generator.
What GPA do I need for college admissions?
GPA needs depend on the college and the program. Many schools care most about core classes and course rigor. Use GPA requirements for college admissions for broad ranges, and check bigger benchmarks in GPA benchmarks for professional programs.
How can I raise my GPA quickly without burning out?
Focus on the classes with the most credits and the biggest grade gaps. You can often gain the most from turning one D into a C or one C into a B. Use study tips for better grades and follow a simple plan from raise my GPA action plan.
Can colleges recalculate my GPA differently than my high school?
Yes. Many colleges recalculate GPA using your transcript grades, often with their own rules. That is why strong grades in hard classes still help you, even if your school scale feels strict. For planning, see GPA requirements for college admissions and keep your records clean with transcript GPA audit guide.