Key Takeaways
| Feature | Unweighted GPA | Weighted GPA |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Typically 0.0–4.0 | Often 0.0–5.0 (or higher) |
| Course Value | All classes are treated equally (an A is always a 4.0). | Advanced courses (AP, Honors, IB) are given extra value. |
| Purpose | Provides a standard measure of academic performance. | Shows academic ambition and success in challenging courses. |
| College View | Colleges use it to compare students from different schools. | Colleges see it as a sign of a student's willingness to take on a rigorous workload. |
Understanding your Grade Point Average (GPA) is a key part of managing your academic journey. The main difference between a weighted and an unweighted GPA lies in how course difficulty is handled. A tool that lets you toggle between these two views can offer powerful insights into your academic standing and help you plan for the future.
Understanding the Basics: Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
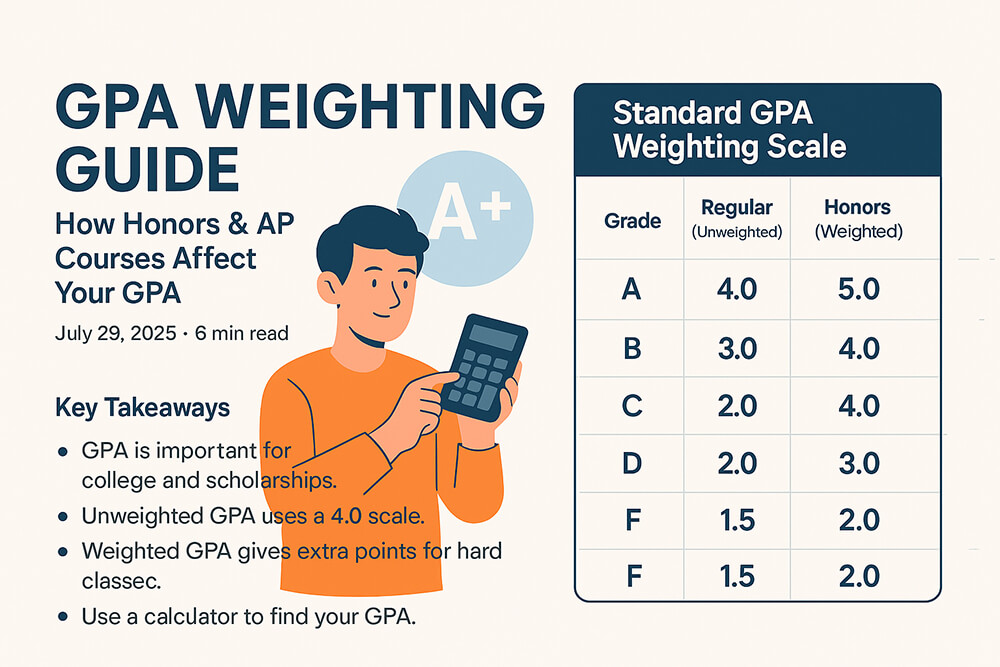
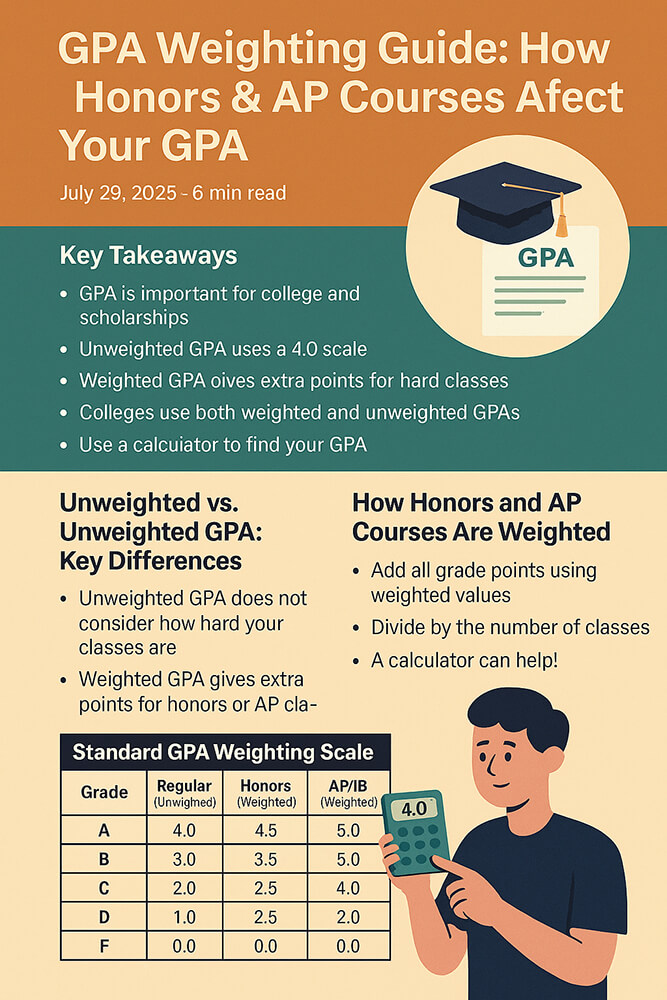
An unweighted GPA is the most straightforward measure of your academic performance. It operates on a simple 4.0 scale, where an 'A' is a 4.0, a 'B' is a 3.0, and so on. This method treats every class the same. An 'A' in a standard art class has the same value as an 'A' in AP Physics. This provides a clear, standardized look at your grades.
A weighted GPA, however, gives extra credit for more difficult classes. This system acknowledges the extra effort required for honors, Advanced Placement (AP), or International Baccalaureate (IB) courses. A student who excels in these challenging classes can earn a GPA higher than 4.0. You can learn more by reading a detailed comparison of weighted vs. unweighted GPA.
A Closer Look at the Unweighted GPA
The unweighted GPA provides a simple average of your grades. It is calculated by converting your letter grades to points on a 4.0 scale, adding them up, and dividing by the number of classes you've taken. For example, if you have three A's (4.0 each) and one B (3.0), your unweighted GPA would be 3.75.
Colleges often use the unweighted GPA as a baseline to compare applicants from various high schools, each with different grading policies. It offers a standardized metric of academic achievement. For a step-by-step walkthrough, see this guide on how to calculate your GPA.
Understanding the Weighted GPA Scale
A weighted GPA scale is designed to reward students for taking on more academic challenges. Most commonly, this scale goes up to 5.0, but some schools may use different systems. On a 5.0 scale, an 'A' in an AP or IB class might be worth 5.0 points, while an 'A' in a standard class remains a 4.0.
This system helps colleges identify students who are not only earning good grades but are also pushing themselves in advanced subjects. It provides a more detailed picture of a student’s academic drive. Explore the nuances of this system with a guide to the 5.0 GPA scale.
GPA Weighting for Honors and AP Courses
The primary purpose of GPA weighting is to properly credit students for the rigor of their coursework. Honors and AP classes demand more time, effort, and critical thinking. By assigning extra points, the weighted GPA reflects this increased difficulty. For example, an 'A' in an AP class might add 1.0 point to your GPA, while an honors class might add 0.5 points.
This weighting system is crucial for college admissions, as it signals a student's readiness for college-level work. For more details, check out this GPA weighting guide for Honors and AP courses.
How to Calculate Your GPA
Calculating your GPA involves a straightforward formula. First, you convert each letter grade into its corresponding grade point value. Then, you sum these points. Finally, you divide the total points by the number of courses taken. This gives you your Grade Point Average.
For a weighted GPA, you would first apply the extra weight to your advanced courses before summing the points. A clear understanding of the GPA formula guide is essential for accurate manual calculations.
Avoiding Common GPA Calculation Mistakes
Simple errors can lead to an incorrect GPA, which can cause unnecessary stress. A frequent mistake is using the wrong point value for a grade or miscalculating the weight for an honors or AP class. Another common issue is incorrectly averaging the grades, especially when courses have different credit values.
Double-checking your math and understanding your school's specific weighting policy are key. To prevent these issues, review a list of common GPA calculation errors to avoid.
Using a GPA Calculator Tool
A GPA calculator simplifies the entire process. By entering your grades and course types, the tool instantly provides both your weighted and unweighted GPA. This removes the chance of manual errors and saves you time.
Our High-School GPA Calculator features a toggle tool that allows you to switch between weighted and unweighted views effortlessly. This feature helps you see how your course choices impact your overall academic profile, aiding in future planning.
Converting Letter Grades to GPA Points
The first step in any GPA calculation is converting letter grades into their numerical equivalents. On a standard 4.0 scale, an 'A' is 4.0, 'B' is 3.0, 'C' is 2.0, and 'D' is 1.0. Some schools also use plus and minus grades, which have their own specific point values (e.g., a B+ might be a 3.3).
Knowing the correct conversion is fundamental. For a complete breakdown, refer to this letter to point GPA conversion guide.
Understanding Quality Points vs. GPA
The terms "quality points" and "GPA" are related but not identical. Quality points are the total points you earn for all your courses combined, calculated before the final division step. To find your quality points, you multiply the grade point value of each course by the number of credits for that course and then sum them up.
Your GPA is the average of these points. It is calculated by dividing your total quality points by your total credit hours. This guide on quality points vs. GPA explains the distinction clearly.
How Credit Hour Weighting Affects Your GPA
Not all classes are worth the same number of credits. A year-long course will have a greater impact on your GPA than a semester-long elective. When you calculate your GPA, you must account for the credit hours of each course. Courses with more credits carry more weight in the final calculation.
This is why earning a good grade in a high-credit course is so important. A detailed explanation can be found in this credit hour weighting GPA guide.
The Impact of Pass/Fail Grades
Pass/Fail courses are typically not included in your GPA calculation. A "Pass" grade grants you the credits for the course, but it does not have a grade point value to be averaged in. A "Fail" grade, however, is often treated as an 'F' and can negatively impact your GPA.
The specific policy can vary by school, so it is always a good idea to check with your academic advisor. Learn more about how pass/fail grades impact your GPA.
GPA Calculations for Different School Systems
High schools can have different academic calendars, such as semesters or trimesters. This can affect how and when your GPA is calculated. For schools on a trimester system, GPA is typically calculated at the end of each of the three terms.
The calculation method remains the same—summing your grade points and dividing by the number of courses or credits—but the timing is different. A trimester GPA calculator can be a helpful tool for students in these systems.
How School Districts Calculate GPA
It is important to know that GPA calculation policies can vary between different school districts. Some may use a 4.0 scale, while others might use a 5.0 or even a 12.0 scale for weighted GPAs. These differences are outlined in a school's profile, which colleges review to understand the context of your GPA.
Understanding your local district's method is key to accurately tracking your academic progress. You can find more information on how school districts calculate GPA.
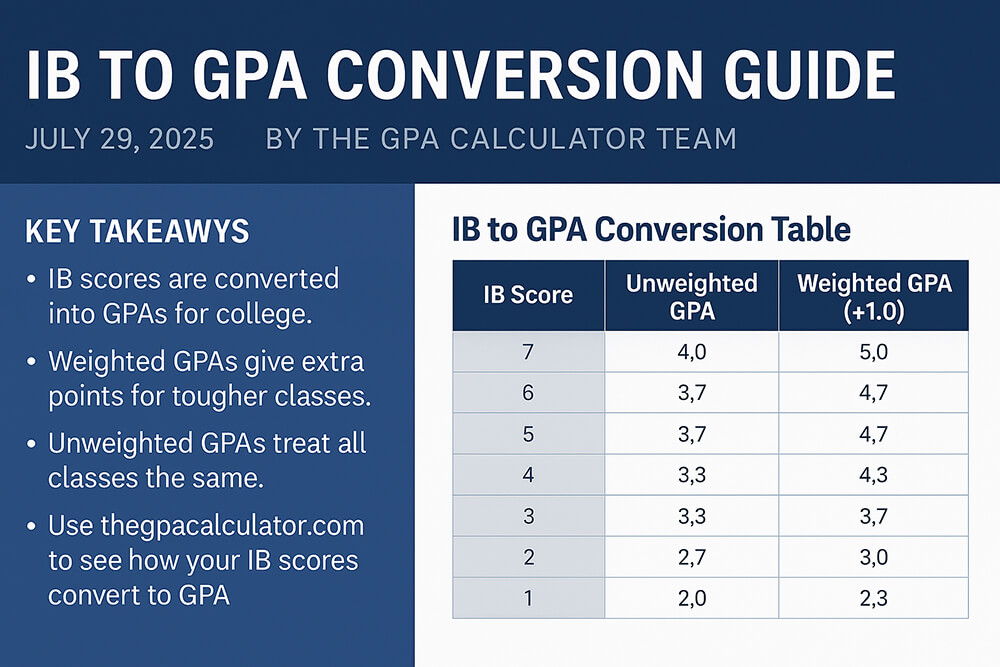
Converting IB Grades to GPA
For students in the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, converting their grades to a standard U.S. GPA scale is essential for college applications. IB grades are awarded on a 1 to 7 scale. Each number corresponds to a specific grade point value on the 4.0 or 5.0 GPA scale.
This conversion allows admissions officers to compare IB students with those from other academic programs. An IB to GPA conversion guide provides the necessary tables and instructions.
Debunking Common Weighted GPA Myths
Several myths surround weighted GPAs. One common misconception is that colleges only look at the weighted GPA. In reality, admissions officers consider both weighted and unweighted GPAs to get a full academic picture. Another myth is that taking many AP classes and getting B's is better than getting A's in regular classes. While rigor is valued, strong performance is crucial.
Getting accurate information helps you make better academic choices. This article on weighted GPA myths debunked clarifies these points.
Understanding GPA Inflation and Deflation
GPA inflation is the trend of average GPAs rising over time, which can make it harder for top students to stand out. GPA deflation is the opposite, where grading standards become stricter. Colleges are aware of these trends and use a school's profile to evaluate the rigor of its grading system.
This context helps them make fair comparisons between applicants from different schools. Learn more about GPA inflation vs. deflation to understand how your GPA is viewed.
How to Perform a Transcript GPA Audit
Regularly reviewing your transcript for accuracy is a good practice. A transcript audit involves checking that all your courses, grades, and credits are correctly listed. You should also verify that the calculated GPA matches your own calculations, for both weighted and unweighted values.
If you find any discrepancies, you should contact your school counselor immediately to have them corrected. Following a transcript GPA audit guide can make this process easier.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main difference between weighted and unweighted GPA? An unweighted GPA is calculated on a standard 4.0 scale where all classes have the same value. A weighted GPA gives extra points for advanced or difficult courses like AP and Honors, often using a 5.0 scale.
How do I use a weighted vs. unweighted toggle tool? You enter your letter grades and specify the course type (e.g., regular, honors, AP). The tool then calculates your GPA. The toggle feature allows you to instantly switch the view between the unweighted (4.0 scale) and weighted (5.0 scale) results.
Do colleges prefer weighted or unweighted GPA? Colleges look at both. The unweighted GPA provides a standardized measure of performance, while the weighted GPA shows your willingness to take on challenging coursework. They use both to get a complete picture of your academic abilities.
What is considered a good GPA? A "good" GPA depends on your college goals. Generally, an unweighted GPA of 3.5 or higher is competitive for many universities. Top-tier colleges often look for unweighted GPAs of 3.8–4.0 or weighted GPAs above 4.0.