Key Takeaways
| What 4.0 scale grades tell you | Why it matters | Quick win |
|---|---|---|
| A 4.0 means straight A’s (unweighted) | It signals strong consistency across classes | Use a high school GPA calculator to verify your real number |
| Weighted GPAs can go above 4.0 | Honors/AP/IB points change the “top” of the scale | Compare both with a weighted vs unweighted GPA guide |
| Credit hours can change everything | One hard class can swing your average fast | Learn the math with credit hour weighting in GPA |
| Small cutoffs feel huge (89 vs 90) | A 1% change can look like a big GPA jump | Check letter to point GPA conversion for your school’s rules |
| A 4.0 is rare, but not always equal | Grade inflation makes GPAs uneven across schools | Understand the context with GPA inflation vs deflation |
| Perfection has diminishing returns | A 3.8–3.9 often performs like a 4.0 in real outcomes | Protect your balance with study tips for better grades |
What 4.0 scale grades really mean
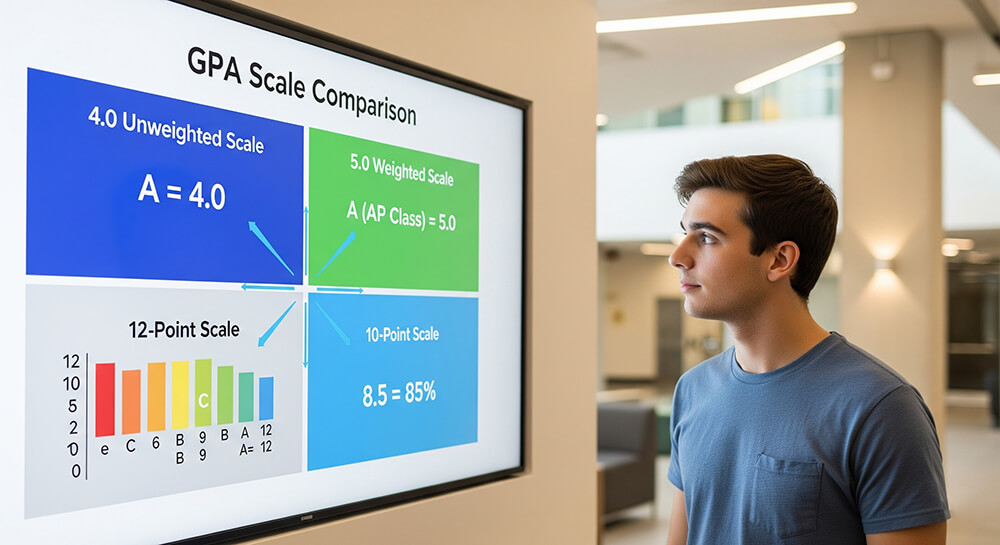
4.0 scale grades turn letter grades into points. A typical system gives A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0, and F = 0.0. A perfect 4.0 GPA usually means straight A’s across your classes on an unweighted scale.
The tricky part is what that number represents. A 4.0 can mean “top student in a tough school,” or it can mean “strong student in a school with easier grading.” Both students worked hard, but the number can hide the details.
A GPA works best when you pair it with course difficulty, credits, and trend over time. The fastest way to get clarity is to run your grades through a trusted tool like the college GPA calculator or the how to calculate GPA guide.
Letter grades to GPA points: the clean conversion
Most schools use a simple conversion. A grade of 90–100% becomes an A (4.0). 80–89% becomes a B (3.0). That sounds fair, but real grading has extra layers like plus/minus, different cutoffs, and course weights.
If your school uses A- and B+, your “B range” can split into multiple point values. That is why two students with close percentages can end up with different GPAs. It is also why the same report card can look different after a school recalculates it.
For the most accurate result, use a chart made for your scale and rules. A strong starting point is letter to point GPA conversion. If you are converting from percentages, percentage to 4.0 GPA conversion helps avoid common mistakes.
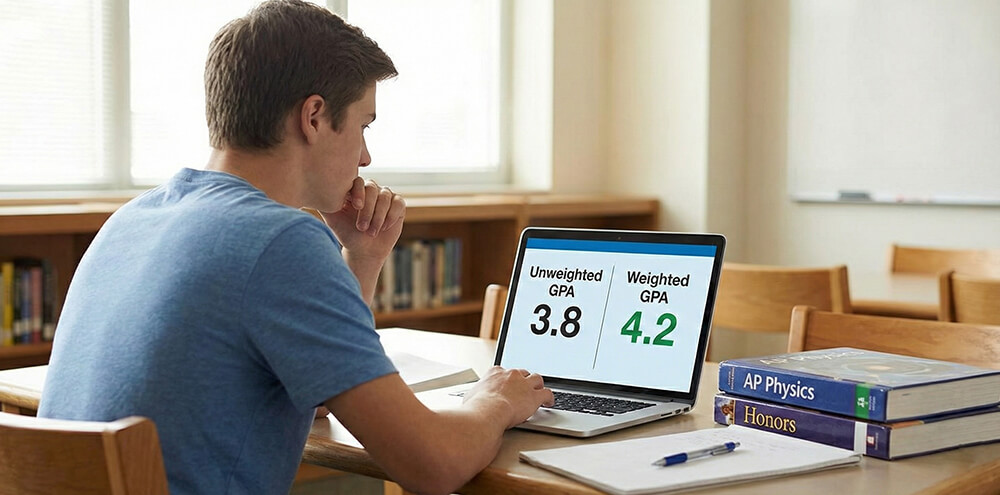
Weighted vs unweighted: why some GPAs go above 4.0
Unweighted GPA is simple: every class tops out at 4.0. Weighted GPA adds extra points for harder classes. Many schools give an honors or AP “A” a boost, so the class can count as 4.5 or 5.0. That is how students end up with GPAs like 4.2 or 4.6.
This difference matters in competitive admissions. A student with a 4.0 unweighted may have all A’s in standard courses. Another student may have a 4.3 weighted because they took harder classes and still earned high grades.
The best way to read the number is to look at both scales. If your transcript shows only one, you can estimate the other using GPA weighting guide for honors and AP and a weighted vs unweighted GPA calculator.
Credit hours and quality points: the math that moves your GPA
GPA is not just “average of grades.” It is an average of quality points. That means credits matter. A 4-credit class affects your GPA more than a 1-credit class.
Here is the core idea:
- GPA points × credit hours = quality points
- Total quality points ÷ total credits = GPA
So an A in a heavy class can lift you fast, and a low grade in a heavy class can drop you fast. This is why students feel one course “wrecked” their GPA, even when most grades stayed high.
If your GPA ever feels confusing, check your math using quality points vs GPA explained and GPA formula guide. When you want to plan a comeback, tools like the semester GPA calculator and cumulative GPA calculator make the impact easy to see.
The 89 vs 90 problem: why tiny gaps feel huge
One big complaint about 4.0 scale grades is how sharp the cutoffs feel. A student with 89% may get a B+, while 90% becomes an A-. That single point can look like a big change in GPA points.
This creates pressure around “magic numbers.” Students chase the cutoff, even when learning is almost the same. The system rewards scoring rules more than growth, especially when the course is hard and the tests are strict.
If this sounds familiar, you are not alone. The healthiest move is to focus on patterns you can control: homework consistency, test prep routines, and asking for help early. If you want a clean plan, use study habit audit checklist and study tips for better grades.
Grade inflation: why a 4.0 can mean different things
Grade inflation happens when average grades rise over time. It can come from policy changes, easier grading, retake rules, or pressure on schools to show better results. The issue is not that students “got worse” or “got better.” The issue is that the same letter grade can stop meaning the same thing.
A 4.0 from a strict school may reflect stronger mastery than a 4.0 from a school with looser grading. Admissions teams know this, which is why they often look at school profile data, course rigor, and class rank when it exists.
If you feel stuck comparing your GPA to someone else’s, shift the focus to what colleges can compare more fairly: course level, trend, and performance in core subjects. Use transcript GPA audit guide to clean up your records and common GPA calculation errors to avoid to catch hidden mistakes.
How rare is a 4.0 GPA today?
A perfect 4.0 still sits near the very top in most schools, but it shows up more often now than it did decades ago. That is why it feels common online. Social media highlights the top students, so it can look like “everyone has a 4.0,” even when that is not true in real life.
A smart way to read rarity is to compare your GPA to typical benchmarks. A 3.0 is often seen as a B average. A 3.5+ usually signals strong work. A 3.8+ can place you in a highly competitive range, especially with hard classes.
If you want to measure your GPA against real targets, check GPA benchmarks for professional programs and GPA requirements for college admissions. If your goal is a flagship public university, flagship university GPA requirements can help you set a realistic number.
High school vs college GPA: why many students drop
A common shock is the GPA drop from high school to college. Many students go from being top of the class to feeling average in the first year. That does not mean you “got worse.” College courses often move faster, test deeper, and give fewer easy points.
Time also changes. More reading, more independence, and less structure can hit hard. A strong student can still struggle if their schedule gets messy.
The best defense is planning, not panic. Use tools that make GPA outcomes clear:
- freshman year GPA predictor to set safe targets
- mid-term grade projection slider to adjust early
- raise my GPA action plan to turn stress into steps
What a 4.0 does for college admissions
A high GPA helps, but schools rarely judge it alone. They look at class rigor, trend, course mix, and sometimes test scores (or test-optional context). Many admissions teams also recalculate GPAs to compare students across different grading systems.
A helpful truth: once you are above a strong threshold (often 3.7+), the extra value of perfection gets smaller. A 3.8 with hard classes and strong activities can beat a 4.0 built on easier choices.
If you are trying to shape the best version of your record, it helps to plan your GPA like a project. Use test optional vs GPA thresholds to understand tradeoffs, and community college transfer GPA guide if your path includes a transfer plan.
What a 4.0 means for grad school and professional programs
Graduate programs care more about GPA than most jobs do. Still, each path has its own “good enough” range. Many programs admit plenty of students below a 4.0, especially when research, experience, and fit are strong.
These pages help set real targets:
- grad school GPA requirements guide for general programs
- medical school GPA averages AMCAS 2024–2025 for pre-med planning
- dental school DAT GPA matrix for DAT + GPA combos
If your GPA is not where you want it, a smart recovery path can include retakes, post-bacc work, or targeted grade replacement. The key is to choose actions that move your core GPA, not just your confidence.
Smart ways to raise your GPA without burning out
Chasing perfect 4.0 scale grades can steal sleep, joy, and curiosity. That trade is not always worth it. A better goal is steady improvement with a repeatable routine.
High-impact moves that work in real life:
- Fix missed points first: late work, small quizzes, small homework
- Protect core classes: math, science, English, major courses
- Get feedback early: office hours, review sessions, tutoring
- Track weekly: one simple checklist beats panic
If you have a rough semester, tools can help you recover without guessing. Use repeat course GPA recalculator to see how retakes change your number. Use grade replacement ROI calculator to pick the smartest class to fix.
International students: converting grades into a U.S. 4.0 scale
International grading systems can be very different. Some countries use 100-point scales, some use 10-point, and some use class rankings. A “good” grade at home may not look obvious in a U.S. GPA format.
Conversion helps you tell your story clearly, but it is never perfect. Different schools convert differently, and some U.S. colleges will recalculate your record using their own rules.
Start with a reliable reference page, then match it to your school’s documents:
- international GPA converter guide for the big picture
- China 100-point to 4.0 scale conversion guide for China-based grading
- UK class system grades to 4.0 GPA conversion for UK results
How to check your GPA fast and avoid common mistakes
GPA errors happen more than people think. The most common ones include using the wrong scale, forgetting credits, mixing weighted and unweighted points, or guessing how plus/minus works.
A fast, accurate workflow is simple:
- Convert grades using the right rule set
- Multiply by credits for quality points
- Add totals and divide once
If you want a clean system that matches most schools, use the GPA conversion charts and tools page, then verify the math with the how to calculate GPA guide. If your grades include non-standard items like pass/fail, use how pass/fail grades impact your GPA to avoid surprises.
For a quick start, the tools at The GPA Calculator cover common setups without extra steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a 4.0 GPA always unweighted?
Not always. Many schools report a weighted GPA by default. A 4.0 weighted can be strong, but it may not mean straight A’s in standard classes. Compare both using a weighted vs unweighted GPA calculator and the weighted vs unweighted GPA guide.
Can you get above a 4.0 GPA?
Yes, on weighted systems. Honors, AP, and IB classes can add bonus points. See common setups in the 5.0 GPA scale guide and GPA weighting guide honors AP.
What is a good GPA if you don’t have a 4.0?
A “good” GPA depends on your goals and your school. Many strong applicants sit in the 3.7–3.9 range. Use GPA requirements for college admissions and flagship university GPA requirements to set a target.
Why does my GPA feel lower than my grades?
Credits and weighting can change the result. One heavy class can pull the average down. Check your math with credit hour weighting GPA guide and quality points vs GPA explained.
Do colleges recalculate GPA?
Many do. Some focus on core courses, some remove weights, and some apply their own scale. A helpful reference is how school districts calculate GPA plus a transcript GPA audit guide to keep your records clean.
Does GPA matter after college?
It matters most for internships, first jobs, and grad school admissions. After that, skills and experience often matter more. If grad school is your path, use grad school GPA requirements guide and GPA benchmarks for professional programs to plan smart.
How do I raise my GPA quickly?
The fastest gains come from improving grades in higher-credit courses and fixing repeated mistakes. Use raise my GPA action plan and study tips for better grades. If retakes are allowed, check repeat course GPA recalculator.
How do I convert international grades to a 4.0 scale?
Start with international GPA converter guide, then use country-specific pages like Indian 10-point to 4.0 conversion or Nigeria 5-point to US 4.0 conversion.