Key Takeaways
| Feature | Description | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Basic GPA Calculation | Your GPA is the total quality points divided by the total credit hours. This simple formula is the foundation of your academic record. | Understanding this helps you track your performance each semester and see how individual grades impact your overall standing. |
| Credit Hour Weighting | Courses with more credit hours have a bigger impact on your GPA. An 'A' in a 4-credit class is worth more than an 'A' in a 1-credit class. | This allows you to prioritize your study time on higher-credit courses to have the greatest positive effect on your GPA. |
| Specialized Calculators | Tools exist for unique situations like repeating a course, transferring schools, pursuing a dual degree, or applying to grad school. | These calculators provide precise answers for complex scenarios, helping you make informed decisions about your academic future. |
| GPA Context | A "good" GPA depends on your major and school. STEM fields often have lower average GPAs than humanities. | Knowing the average for your field helps you accurately benchmark your performance against your peers. Generally, a GPA of 3.0 or higher is considered good. |
Understanding the Basics of Your College GPA
Your Grade Point Average (GPA) is a key number in your college life. It shows your overall academic performance. Learning how to figure it out is the first step to managing your grades. Simple tools can help you stay on top of this important metric.
How to Calculate Your GPA: A Simple Guide
Calculating your GPA is a direct process. You take the grades you earn in your classes and turn them into numbers. Then, you find the average. This gives you a single number that represents your hard work. A college GPA calculator makes this process fast and easy, removing guesswork.
The GPA Formula Explained
The math behind your GPA is simple. First, you find your total quality points. You get these by multiplying your grade's point value by the course's credit hours. Then, you divide that total by the number of credit hours you took. This is the core GPA formula guide that all colleges use.
Converting Letter Grades to Grade Points
Every letter grade has a number value. An 'A' is usually a 4.0, a 'B' is a 3.0, and so on. Schools also use plus (+) and minus (-) grades, which have their own values. For example, a 'B+' might be a 3.3 and an 'A-' a 3.7. This letter to point GPA conversion guide is the first step in any calculation.
Understanding Quality Points
Quality points are the building blocks of your GPA. They give weight to your grades based on how many credits a class is worth. A good grade in a class with many credits gives you more quality points. Learning the difference between quality points vs. GPA explained helps you see the true impact of each course.
The Importance of Credit Hours
Not all classes are equal. The number of credit hours a course has is very important. It tells you how much that class will affect your final GPA. Understanding this helps you plan your schedule and your study time wisely.
Why Credit Hour Weighting Matters
The principle of credit-hour weighting in your GPA is simple. A 4-credit science lab will change your GPA more than a 1-credit gym class. This system makes sure your GPA reflects your work in your most demanding classes. It rewards you for doing well in the courses that are central to your degree.
How Pass/Fail Classes Affect Your GPA
Some classes are graded as Pass or Fail. These courses do not use the A-F letter system. A "Pass" grade gives you credit for the class, but it does not get factored into your GPA. A "Fail" grade, however, can count as a 0.0 and may lower your GPA. Knowing how pass/fail grades impact your GPA is key when choosing electives.
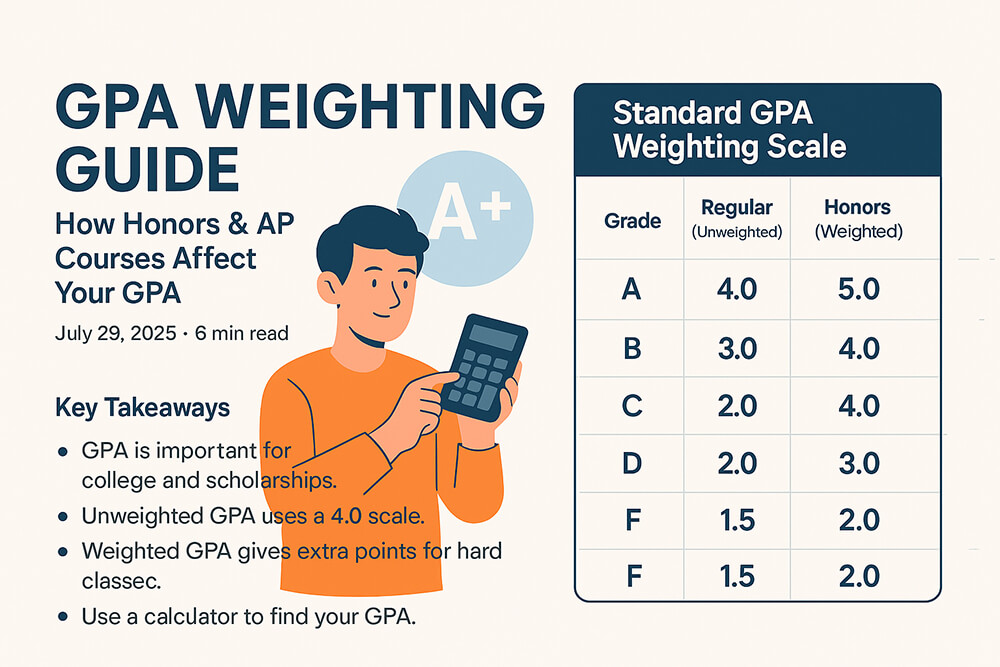
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
Colleges often talk about two types of GPA: weighted and unweighted. An unweighted GPA is on a simple 4.0 scale. A weighted GPA gives extra points for harder classes, like Honors or AP courses. Knowing the difference helps you understand your academic standing.
What's the Difference?
The main difference between weighted vs. unweighted GPA is how they treat tough classes. An unweighted GPA treats every class the same. An 'A' is always a 4.0. A weighted GPA gives you more points for an 'A' in an advanced class, often a 5.0. This rewards students for taking on more challenging work.
A Guide to GPA Weighting for AP/Honors
Schools use weighted GPAs to recognize the extra effort of advanced courses. An 'A' in an AP class requires more work than an 'A' in a standard class. The GPA weighting guide for Honors and AP shows how these extra points can raise your overall GPA and make your transcript look more impressive to colleges.
Debunking Weighted GPA Myths
Many students have questions about weighted GPAs. Do all colleges use them? Does a weighted GPA guarantee admission? It is important to separate fact from fiction. Our guide on weighted GPA myths debunked clears up common confusion and helps you understand how admissions officers really view your grades.
Using a Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA Calculator
To see the real impact of your advanced classes, you need the right tool. A weighted vs. unweighted GPA calculator lets you see your GPA both ways. This helps you understand how different colleges might view your academic record and allows you to present your achievements accurately.
Advanced & Specialized GPA Calculators
Your college journey can have unique situations. You might retake a class, transfer schools, or aim for special honors. For these moments, standard GPA math is not enough. Specialized calculators give you the clear answers you need to make smart choices.
Planning for Your Future: The Last 60 Credits GPA Calculator
Graduate schools often focus on your most recent grades. They want to see your performance in your junior and senior years. A last 60 credits GPA calculator computes this specific average. It helps you see if you meet the entry requirements for master's or Ph.D. programs.
Fixing a Bad Grade: The Repeat Course GPA Recalculator
One bad grade can feel like a big setback. Many schools let you retake a class to improve your GPA. However, each school has different rules for this. A repeat course GPA recalculator shows you exactly how a new grade will change your GPA based on your school's policy.
For the Ambitious: The Dual Degree GPA Splitter
Studying for two degrees at once is a big challenge. You often need to track your GPA for each major separately. A dual degree GPA splitter does this work for you. It separates your courses to show your GPA in each field, ensuring you stay on track for both degrees.
Changing Schools: The Transfer Credits GPA Integrator
When you move to a new college, your GPA usually starts over. Your old grades don't count toward your new GPA at the new school. A transfer credits GPA integrator helps you calculate the transfer GPA that admissions offices will look at, giving you a clear picture of your standing before you apply.
Aiming High: The Dean's List Eligibility Checker
Making the Dean's List is a great honor. To qualify, you usually need a high GPA and a full course load, often a 3.5 GPA with at least 12 credits. Requirements can vary by school. A Dean's List eligibility checker lets you input your school's rules to see if you are on track to earn this academic award.
Understanding Different GPA Scales and Systems
The standard 4.0 GPA scale is common, but it's not the only one. Some high schools use a 5.0 scale for weighted grades. International programs like the IB have their own systems. Knowing how these different scales work is important for accurately representing your academic achievements.
Beyond the 4.0: The 5.0 GPA Scale Guide
Some high schools use a 5.0 scale to give more weight to advanced classes. This allows students in Honors or AP courses to earn a GPA above a 4.0. A 5.0 GPA scale guide explains how this system works and how colleges convert it back to a 4.0 scale for admissions.
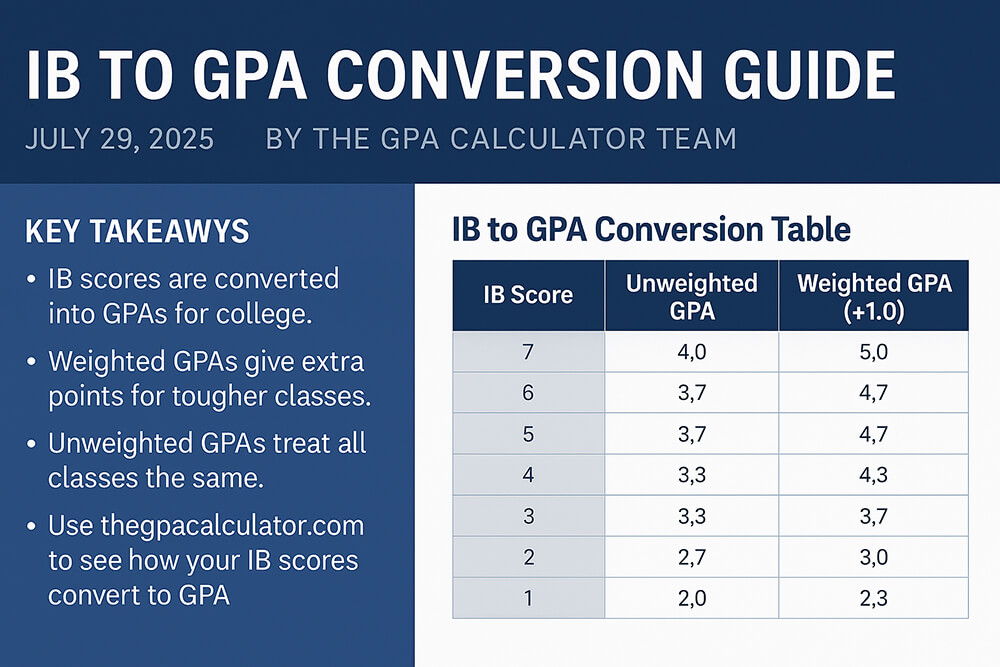
From Global to Local: IB to GPA Conversion
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program uses a 1-7 scoring system. Students with IB scores need to convert them to a traditional GPA when applying to U.S. colleges. An IB to GPA conversion guide provides the information needed to translate these scores, ensuring your hard work is understood by admissions officers.
How Different School Districts Calculate GPA
GPA calculation rules can change from one place to another. Some districts may weigh courses differently or use unique scales. Understanding how school districts calculate GPA is important for high school students. It helps you know exactly where you stand and how colleges will view your transcript.
The Trimester GPA Calculator
Colleges on a trimester or quarter system have a different academic calendar. This can change how and when your GPA is calculated. A trimester GPA calculator is designed for this system. It helps students accurately track their GPA each term and project their cumulative average for the year.
Common Pitfalls and Strategic Planning
Managing your GPA is about more than just getting good grades. It involves avoiding simple mistakes and planning ahead. Knowing the common errors in GPA calculation and understanding long-term trends can help you protect your academic record and reach your goals.
Avoiding Common GPA Calculation Errors
Simple mistakes can lead to an incorrect GPA. Forgetting to factor in credit hours or miscalculating plus/minus grades are frequent issues. A guide to common GPA calculation errors to avoid helps you double-check your math. This ensures the GPA you calculate is the same one that will appear on your transcript.
The Truth About GPA Inflation and Deflation
Average GPAs have been rising over the years, a trend called grade inflation. This can change what is considered a "good" GPA. Understanding GPA inflation vs. deflation gives you context. It helps you see how your GPA compares to students from other schools and other generations.
A Guide to Auditing Your Transcript GPA
Your official transcript is the final record of your grades. It is smart to check it for accuracy. A transcript GPA audit guide shows you how to review your transcript. You can make sure every grade and credit hour is correct, preventing any surprises when you apply for jobs or graduate school.
Planning Ahead: The Freshman Year GPA Predictor
Your first year of college sets the foundation for your cumulative GPA. A strong start makes it easier to maintain a high average later on. The freshman year GPA predictor is a tool for new students. It helps you set goals and see how your first-year grades will impact your entire college career.
High School GPA Matters Too
Your college journey begins in high school. Your high school GPA is a major factor in college admissions. Using a high school GPA calculator helps you track your progress from the start. It ensures you are on the right path to get into the college of your choice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a good college GPA? A GPA of 3.0 or higher is generally considered good. Many scholarships and graduate programs require at least a 3.0. A GPA of 3.5 or above is often considered excellent and may qualify you for honors like the Dean's List.
How do I calculate my GPA for one semester? To calculate your semester GPA, first convert each letter grade to its point value (e.g., A=4.0, B=3.0). Multiply each grade's point value by the number of credit hours for that course to get the quality points. Finally, add up all your quality points and divide by the total number of credit hours you took.
Do Pass/Fail classes affect my GPA? Usually, no. A "Pass" grade earns you credit but is not included in your GPA calculation. However, a "Fail" grade is often treated as a 0.0 and will lower your GPA. It is important to check your school's specific policy.
Can I fix my GPA by retaking a class? Many universities allow you to repeat a course to earn a better grade. School policies vary widely. Some will replace the old grade with the new one, while others might average the two grades together. A repeat-course calculator can show you the potential impact.
How do graduate schools look at my GPA? Graduate schools look closely at your cumulative GPA as a sign of academic readiness. Many programs require a minimum GPA, often a 3.0 or higher. They may also calculate the GPA for your last 60 credit hours (junior and senior years) to see your more recent performance.