STEM vs. Non-STEM GPA: Understanding the Difference in College Grades
Students in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) often have lower grade point averages (GPAs) than students in non-STEM fields. This guide explains why this happens and what it means for you.
Key Takeaways
| Factor | Insight |
|---|---|
| The GPA Gap | STEM majors often have lower average GPAs than humanities or social science majors. Studies show this gap can be significant. |
| Reason 1: Grading Style | STEM courses usually have right-or-wrong answers. This makes grading very objective. Humanities classes often grade essays and projects, which can be more subjective. |
| Reason 2: "Weeder" Classes | Early STEM classes are often very hard. They are designed to be tough to see who will continue in the major. |
| Reason 3: Building Blocks | STEM subjects build on each other. You must understand the first topic to learn the next one. This makes it hard to catch up if you fall behind. |
| What Employers Think | Many companies know that a 3.0 GPA in engineering is different from a 3.0 in another field. They often care more about your skills than just your GPA. |
| How to Manage | Use tools to track your grades. A college GPA calculator can help you see where you stand. |
The GPA Gap: STEM vs. Non-STEM Majors
Data shows a clear difference in grades between study areas. STEM students tend to earn lower GPAs. For example, chemistry and math majors often have some of the lowest average GPAs. On the other hand, majors like education and languages often have the highest. This is not because one group of students is smarter than the other. It is because the subjects are very different. Understanding this gap helps you set fair goals for your own grades. You can see your progress with a GPA trend graph generator.
Why Is There a GPA Difference?
The way classes are graded is a big reason for the GPA split. In a math or science class, your answer is either correct or incorrect. This leaves little room for extra points. In a humanities class, a professor grades your writing or ideas. This can be more open to interpretation. Also, many STEM programs have very difficult introductory courses. These "weeder" classes are meant to challenge students early on. This structure can lead to lower grades for even very smart students.
How to Calculate Your GPA Correctly
To understand your grades, you need to know how to find your GPA. The basic process is simple. First, change each letter grade to its point value (A=4, B=3, etc.). Then, multiply that point value by the number of credits for the class to get your quality points. Finally, add up all your quality points and divide by your total credit hours. For a step-by-step process, use a how to calculate gpa guide. Avoiding simple mistakes is key, so it helps to read about common gpa calculation errors to avoid.
Using a Dual-Degree GPA Splitter for Clarity
Many students study more than one subject. You might have one major in STEM and another in a non-STEM field. This can make your overall GPA confusing. A dual-degree GPA splitter is a tool that can help. It lets you see your GPA for each major separately. This gives you a better picture of your performance in different areas. It is also useful for graduate school applications, which may ask for your GPA in your specific field of study.
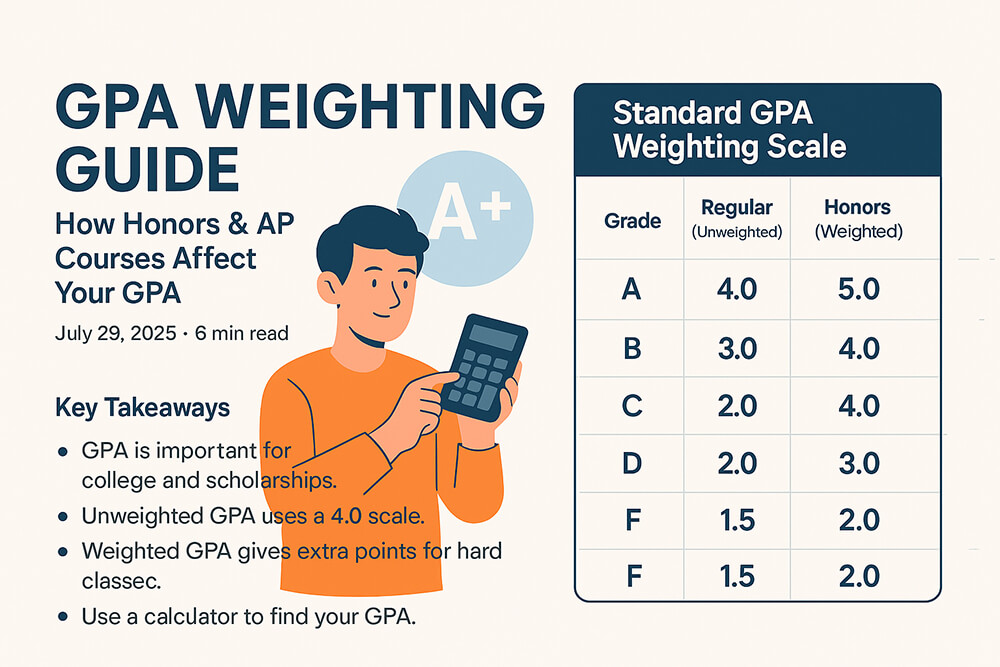
The Role of Weighted Grades in the GPA Split
Some schools use weighted GPAs. This means that harder classes, like Advanced Placement (AP) or Honors courses, are given more weight. An A in an AP class might be worth 5.0 points instead of 4.0. This can help students in tough STEM classes. However, not all colleges look at weighted GPAs. It is important to know the difference between weighted vs unweighted gpa. Understanding how your school handles this can help you plan your classes. A gpa weighting guide honors ap can provide more details.
Managing Special Grades That Impact Your GPA
Sometimes you may have grades that are not standard letters. A "Pass" or "Fail" grade is one example. These usually do not affect your GPA, but they do appear on your transcript. An "Incomplete" is another special case. Knowing how pass fail grades impact your gpa is important. If you have to retake a class, a repeat course gpa recalculator can show you how a new grade will change your GPA. For complex situations, a guide on gpa planning for incomplete grades can be very helpful.
Tools for Tracking Your GPA Over Time
Keeping track of your GPA is easy with the right tools. A semester gpa calculator helps you see your grades for one term. To see the big picture, you can use a cumulative gpa calculator. These tools let you input your grades and credits to get an instant result. Some tools even let you see what grades you need in the future to reach a target GPA. Using a mid term grade projection slider can help you plan for the rest of the semester.
How Transfers and Study Abroad Affect Your GPA
Your academic journey may include classes from different schools. You might transfer from another college or study in another country. It is important to know how these grades will be counted. A transfer credits gpa integrator can help you see how your old classes will affect your new GPA. Similarly, a study abroad grades gpa integrator helps with courses taken overseas. Every school has its own rules, so always check with your advisor.
Planning for the Future with Your GPA
Your GPA is important for future opportunities. Many graduate schools look at your GPA from your last 60 credits. A last 60 credits gpa calculator can help you figure this out. Your GPA can also determine if you make the Dean's List. You can use a deans list eligibility checker to see if you qualify. It is never too early to start planning. A freshman year gpa predictor can help you set goals from the start of your college career.
Grade Inflation and the STEM GPA Split
Grade inflation means that the average GPA at colleges has been rising over time. However, this trend is less common in STEM fields. Science and engineering departments often keep stricter grading standards. This can make the GPA gap between STEM and non-STEM majors even wider. For more information, you can read about gpa inflation vs deflation. This context is important when comparing your GPA to students in other fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is a 3.0 GPA in an engineering major considered bad? A 3.0 GPA in a tough engineering program is often seen as a solid achievement. Employers and graduate schools in technical fields usually understand the difficulty of STEM majors and view GPAs in that context.
2. Why are humanities GPAs often higher than STEM GPAs? Humanities courses frequently use essays and projects for grades, which can be graded more subjectively than the right-or-wrong tests in many STEM classes. This difference in assessment style is a primary reason for the GPA gap.
3. Do employers know that STEM GPAs are usually lower? Yes, many employers, especially in the tech and engineering industries, are aware of the grading differences between majors. They often place more importance on practical skills, internships, and project experience than on GPA alone.
4. How can I calculate the GPA for only my major-specific courses? To calculate your major GPA, you only include the courses required for your major. You add up the quality points for just those classes and divide by the total number of credit hours for them. A college GPA calculator can often be filtered to show your major-only GPA.